Black holes - places with the highest gravity in the universe, where even light cannot escape
Black holes are the most gravitating and densest places in the universe. The gravity of these is so much that even light cannot escape it. The huge mass of these black holes store in a very small volume, and due to the enormous gravitational pull caused by this huge mass, no particle or matter can escape from a black hole. Black holes are often formed due to the massive supernova explosions that occur due to the gravitational collapse of the cores of massive stars at the end of their lifespan, and neutron stars also create by these supernova explosions of small stars.
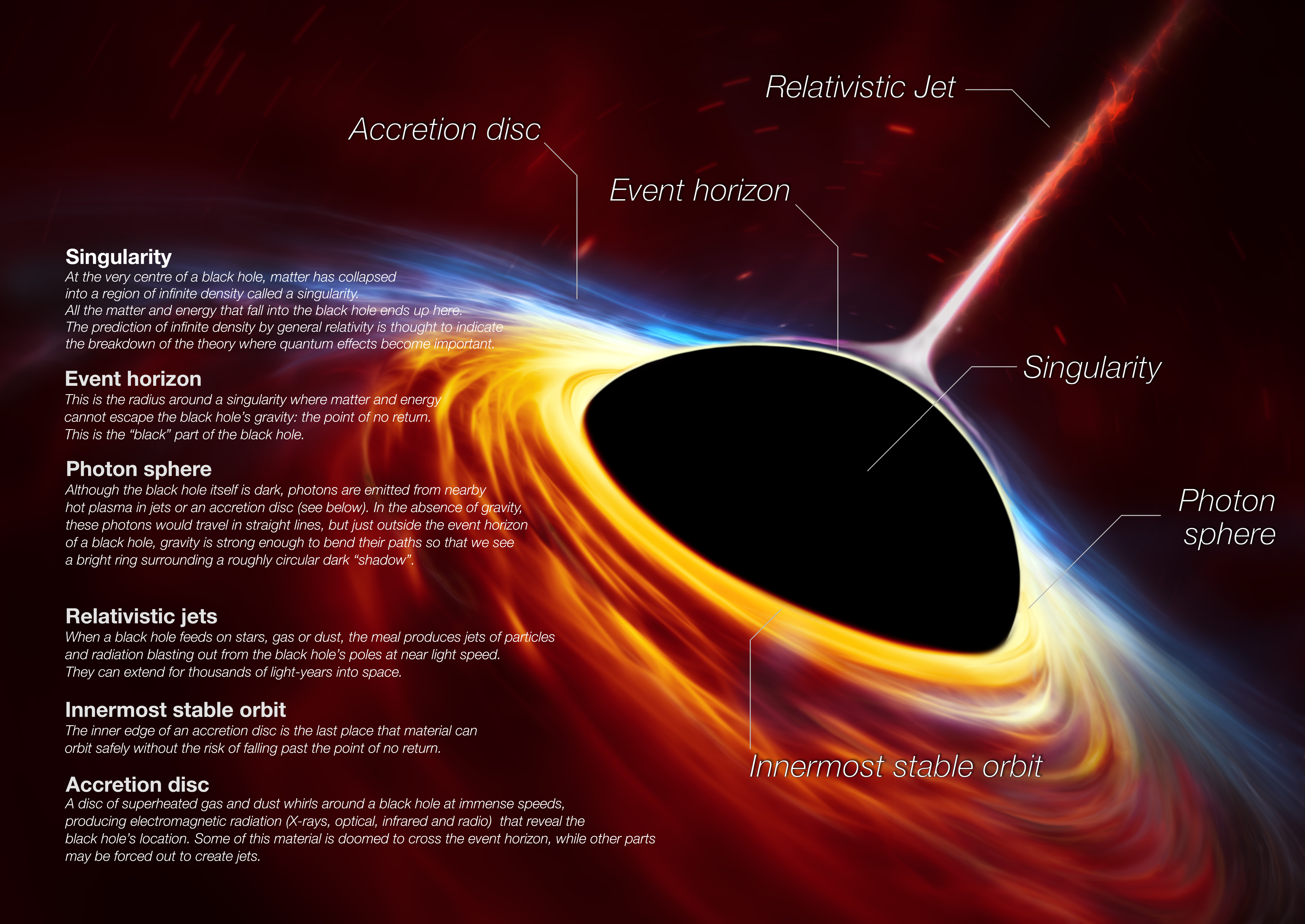
A black hole basically has 2 main structural parts. If they are,
1. Singularity
"Singularity" is when the mass of any matter compresses to an infinitesimally small point, and eventually, all concepts of time and space will ultimately collapse. The theoretical physicist known as the great genius of the 20th century, Mr. "Albert Einstein," was presented in 1916. The "general theory of relativity" has predicted this and the existence of black holes for the first time.
2. Event horizon
the bright spherical region around the black hole, and even light cannot escape from this boundary region. It does not have a physical plane, and the escape velocity here is equal to the speed of light.
The first definition of a black hole or "black hole" was made by an American astronomer, "John Wheeler," in 1967. In 1971, the black hole in the center of the binary star system named "Cygnus X-1" was discovered. The hole made history as the first known black hole and is located 7000 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. In contrast, studying the X-ray fluxes emitted by the binary star system "Cygnus X-1", the black hole discovers.
Cygnus X-1 seen by Chandra X-ray Observatory
Classification of black holes
Solar mass is used to calculate the size of black holes. Here, the mass amounts are calculated relative to the mass of our Sun, 1.9891 × 1030 kg (333000 times the mass of the Earth).
The equation used to calculate solar mass units
2. Intermediate-mass black holes - have a mass between 100-1000 solar masses.
3. Supermassive black holes - Solar masses range from millions to billions.
4. Miniature black holes/Micro black holes have a mass of 3.3 (10-23 kg) solar mass.
Astronomers believe there are over 100 million black holes of various sizes in our Milky Way galaxy alone. The black hole belonging to the "Supermassive black hole" called "Sagittarius A*" is in the center of the Milky Way galaxy and is located 26,000 light-years away from Earth. The mass of this black hole with a radius of about 12 million kilometers is 4.1 million times the mass of the Sun. The first image of a black hole was captured in 2019 by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) network. This black hole is M87 (Messier 87 /Virgo A / NGC 4486), which is 55 million light-years away from Earth. Also known by the names.) is the black hole belonging to the supermassive black hole located at the center of the elliptical galaxy.






Comments
Post a Comment